Have you ever wondered how some large-scale construction projects seem to go up with incredible speed, efficiency, and precision? The answer often lies in the innovative world of Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEBs). Far from simple “sheds,” PEBs are revolutionizing the construction industry, offering a smarter, faster, and more cost-effective way to build.
But what exactly is a PEB, and what goes into its structure and design? Let’s dive in!
What is a Pre-Engineered Building (PEB)?
At its core, a Pre-Engineered Building (PEB) is a complete building system where all components are designed and fabricated off-site, in a controlled factory environment. These meticulously engineered parts are then transported to the construction site and efficiently assembled using bolted connections.
The key differentiator here is the “pre-engineered” aspect. Unlike traditional construction where design and fabrication happen more organically on-site, PEB Structure and design are precisely designed and manufactured to exact specifications, optimizing every piece of steel and every connection for its specific role. This leads to remarkable efficiency and predictability in the construction process.
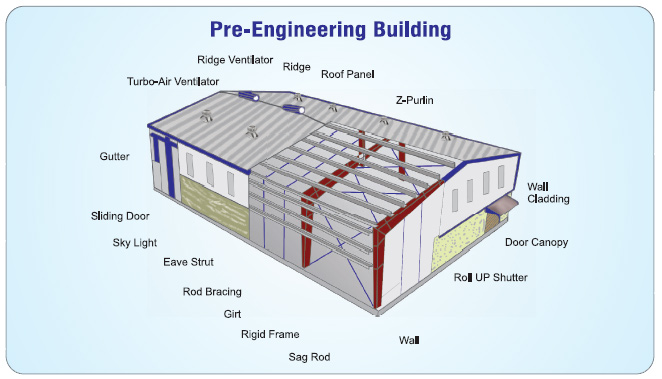
The Core Components of a PEB Structure
A PEB might look simple, but it’s a sophisticated system composed of several key elements working in harmony:
- Main Frames (Primary Members): These are the backbone of any PEB. Typically made from tapered built-up I-sections, these rigid frames form the main structural skeleton. Columns and rafters are designed to carry the primary loads, and their custom engineering ensures they meet the specific requirements of the building’s span and usage.
- Secondary Members: These elements support the roof and wall panels and transfer loads to the main frames.
- Purlins: These are Z and C-shaped sections that span between the rafters to support the roof cladding.
- Girts: Similar to purlins, girts are Z and C-shaped sections that run horizontally along the walls to support the wall cladding.
- Eave Struts: These are strategically placed at the eaves to provide support for both roof and wall panels.
- Roof and Wall Panels (Cladding): These form the building’s envelope, offering protection from the elements and contributing to its aesthetic appeal.
- Metal Sheets: Commonly used materials include Galvalume (a zinc-aluminium alloy coated steel) and Pre-Painted Galvanized Iron (PPGI). These are durable, lightweight, and available in various colors.
- Insulated Sandwich Panels: For enhanced thermal insulation, especially in environments requiring temperature control, composite panels with an insulation core (like PUF or Rockwool) sandwiched between metal sheets are used.
- Bracing Systems: Crucial for structural stability, bracing systems resist lateral forces such as wind and seismic activity. They include:
- Rod Bracing: Steel rods diagonal across bays.
- Cable Bracing: Similar to rod bracing but with cables.
- Portal Bracing: Often used when cross-bracing isn’t feasible due to access requirements.
- Accessories: These are the elements that add functionality and customization to the PEB. This can include:
- Skylights for natural lighting
- Ventilators for air circulation
- Louvers, windows, and roll-up doors
- Mezzanines for additional floor space
- Canopies for covered outdoor areas
The PEB Design Process: From Concept to Completion
The “pre-engineered” aspect is where the magic truly happens. The design process for a PEB is highly systematic and technologically driven:
- Initial Client Consultation & Requirements Gathering: It all begins with understanding the client’s vision. This includes the building’s purpose, desired dimensions, specific load requirements (live load from occupants/equipment, dead load from the structure itself, wind load, seismic load), and adherence to local building codes (e.g., Indian Standards for Chennai’s specific wind and seismic zones).
- Conceptual Design & Feasibility Study: Preliminary layouts are drawn, and a feasibility study is conducted. This stage involves initial cost estimations and a high-level assessment of structural viability.
- Detailed Engineering Design: This is the most intensive phase.
- Software Reliance: Advanced structural analysis software like STAAD.Pro, ETABS, and SAP2000 are indispensable. These tools allow engineers to perform complex calculations, simulate various load conditions, and optimize the design.
- Load Calculations: Every potential force on the building is meticulously calculated, from the weight of the roof and snow (if applicable) to the pressure of high winds and potential earthquake forces.
- Optimized Design: Engineers strive for the most efficient use of steel, minimizing material waste without compromising strength or safety. Every beam, column, and connection is sized and detailed precisely.
- Connection Design: A critical aspect is designing the bolted connections. These must be strong, reliable, and straightforward to assemble on-site.
- Shop Drawings & Fabrication Details: The output of this phase includes detailed shop drawings and fabrication instructions that guide the manufacturing process.
- Manufacturing/Fabrication: Once designs are finalized, components are manufactured in a controlled factory environment. This ensures precision cutting, welding, drilling, and application of corrosion-resistant coatings. Strict quality control procedures are maintained throughout this stage.
- Logistics & On-Site Assembly: The fabricated components are carefully packaged and transported to the construction site. Due to the pre-engineered nature and bolted connections, the on-site erection process is remarkably fast and efficient, often requiring less heavy machinery and skilled labor compared to traditional construction.
Key Advantages and Benefits of PEB Structures
Why are PEBs becoming the preferred choice for so many projects, especially in a rapidly developing region like Chennai and across India?
- Speed of Construction: This is arguably the biggest advantage. Off-site fabrication and streamlined on-site assembly dramatically cut down project timelines, leading to quicker occupancy and return on investment.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduced labor costs, minimal material waste, and predictable pricing due to standardized processes contribute to significant cost savings.
- Design Flexibility & Customization: While they are “pre-engineered,” PEBs offer surprising versatility. They can be adapted for various architectural styles and functional requirements, from large clear spans needed for warehouses to multi-story office buildings.
- Durability & Longevity: Built with high-quality steel and often featuring corrosion-resistant coatings, PEBs are designed for long-term performance and resistance to harsh weather conditions.
- Energy Efficiency: The option to incorporate insulated sandwich panels and efficient ventilation systems makes PEBs highly energy-efficient, leading to lower operational costs.
- Sustainability: Reduced on-site waste, precise material usage, and the recyclability of steel make PEBs a more environmentally friendly construction choice.
- Single-Source Responsibility: Often, a single PEB manufacturer handles the design, fabrication, and sometimes even the erection, simplifying project management and accountability.
- Expandability: PEBs are inherently designed for future expansion, making it easier to add bays or sections if your business needs grow.
Common Applications of PEB Structures
The versatility of PEBs means they are suitable for a vast array of applications:
- Warehouses and Logistics Centers: Their large clear spans are ideal for storage and movement of goods.
- Factories and Industrial Buildings: Robust and customizable for various manufacturing processes.
- Showrooms and Commercial Complexes: Offering modern aesthetics and functional spaces.
- Sports Arenas and Gymnasiums: Providing large, unobstructed spaces.
- Aircraft Hangars: Catering to the need for expansive, clear spans.
- Office Buildings: Multi-story PEB systems are increasingly used for modern office spaces.
- Agricultural Buildings: Durable and cost-effective solutions for farming needs.
- Retail Stores: Quick to erect, allowing businesses to open faster.
Conclusion
Pre-Engineered Buildings or PEB Structure design are more than just a trend; they represent a significant leap forward in construction methodology. By combining precision engineering, efficient manufacturing, and rapid assembly, PEBs offer a smart, efficient, and reliable solution for modern building needs. Whether you’re looking to build a vast warehouse, a new factory, or a contemporary commercial space, considering a PEB could be your most strategic move.
Ready to explore the possibilities of PEB for your next project? Connect with a PEB specialist today to see how this innovative construction method can bring your vision to life, faster and more efficiently than ever before.